Assessment of the Fireside Performance of Various Coals
Introduction
Microbeam Technologies, Inc. (MTI) specializes in evaluating the impacts of fuel properties on the fireside performance of various types of coals and biomass fuels. Our unique expertise has helped guide numerous clients worldwide to evaluate and optimize their fuels. This expertise extends to various types of power plants from small to large-scale systems. MTI’s analytical methods and proprietary performance indices are tailored to determine and predict the impact of ash-related materials on coal-fired plant fireside performance. Our vast fuel expertise includes coals of all ranks, energy crops, and various types of biomass and waste materials.
Background
Figure 1. (Right) Deposit formation on the surface of Microbeam’s air-cooled deposition probe. The probe was placed in the reheater section of a combustion plant boiler during an on-site field test conducted by MTI. The accumulated deposits were later removed and analyzed in MTI’s scanning electron scanning microscope (SEM).
The design, performance, and reliability of combustion and gasification systems are impacted by the abundance and form of the ash-forming components in fuels. During combustion, the fuel impurities (ash-forming components) are transformed in the flame to form ash-intermediate materials (vapors, liquids, and solids). These ash-intermediates are entrained with the bulk gas flow through the boiler.
As the heat is extracted, the vapor phase materials condense on the surfaces of particles or condense homogeneously to form very small submicron sized particles. The liquid particles will cool and solidify during gas cooling. The ash intermediates are transported to heat transfer surfaces by inertial impaction, diffusion, and thermophoresis.
As the deposits grow, they will become insulated from the heat transfer surface and increase in temperature. The deposited particles begin to melt and sinter. The sintering process increases the strength of the deposited materials and is dependent upon the viscosity of the liquid phase materials. The chemical and physical properties of the ash intermediates contribute to the formation of deposits in the radiant section of the boiler wall as slag deposits and in the convective pass as fouling deposits. The transformations also impact the performance particulate control systems.
Case Study: Fireside Performance Assessment of Possible Fuels
An international power company contacted Microbeam for assistance in determining the fireside slagging and fouling characteristics of ash produced from the combustion of various selected coals. Combustion testing in a small-scale pulverized coal combustor was used to perform coal combustion testing to produce size classified ash samples for subsequent analysis and testing. The ash materials produced were analyzed to determine the 1. size composition distributions, 2. ash sintering and 3. melting behavior.
As the deposits grow, they will become insulated from the heat transfer surface and increase in temperature. The deposited particles begin to melt and sinter. The sintering process increases the strength of the deposited materials and is dependent upon the viscosity of the liquid phase materials.
Service and Solution
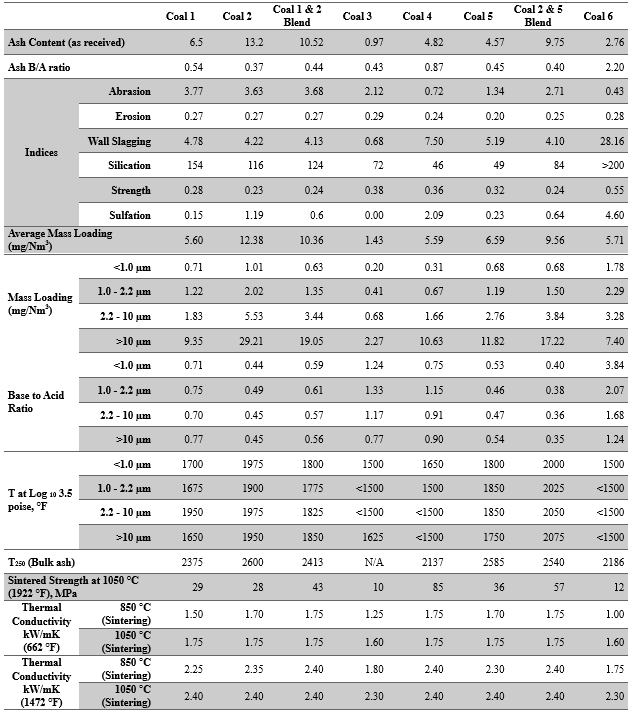
Microbeam performed standard analyses and the proprietary advanced analyses on the samples to obtain the data needed for the calculations of the fireside performance indices related to wear, slag flow, wall slagging, high temperature and low temperature fouling, and strength. In combination with the fireside performance indices, the combustion ash materials characterization results were used to determine the potential for ash deposits to accumulate, develop strength, and impede heat transfer. Examples of key results in this work are presented in Table 1. These results were used to identify key ash transformation and deposition mechanisms associated with the various selected coals.
Table 1. Summary of coal and blend analysis and testing results.
Deliverables
Evaluation of each fuel’s potential for ash deposition determined through various MTI methods including:
Analysis of fuel through laboratory testing and SEM analysis
Fireside performance indices for each fuel including the fuel’s potential for:
Wear, slag flow, wall slagging, high temperature and low temperature fouling, and strength development
Guidance on how each fuel might operate in the client’s system including general performance and potential issues.